Therapeutic focus areas

Neurological and neurodegenerative impairments and diseases
- Stroke
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
- Concussion
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI)
- Dementia
- Post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC)
- Cerebral palsy (CP) with cognitive deficits
- Cognitive symptoms post Chemotherapy
Neurodevelopmental disorder
- ADHD
Psychiatric disorders
- Depression
- Schizophrenia
- Auditory hallucinations
- Addiction disease
- and others
Neurological and neurodegenerative impairments and diseases
-

Stroke
Cognitive deficits play a significant role in stroke rehabilitation, affecting various aspects of cognitive function, including memory, speech, executive functions, as well as motor and visual skills. Stroke stands as the foremost cause of disability in the United States, afflicting 800,000 individuals annually. Fortunately, advancements in stroke treatments have increased survival rates, offering hope for recovery. Tailored therapies and goal-driven programs can help individuals overcome the impact of stroke. Within this context, computer-aided cognitive training emerges as a valuable tool, aiding in the rehabilitation process and fostering cognitive improvement.
-
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) occurs when a hit or jolt to the head or body harms the brain. TBI can be mild, moderate or severe. A more serious TBI can cause long-term challenges or death. TBI can cause a wide range of changes that affect thinking, sensation, language, emotions, and physical abilities. Comprehensive, customized rehabilitation options enable survivors to overcome their challenges and reclaim their lives. An estimated 1.5 million Americans suffer TBIs each year, and more than 5 million people currently live with a TBI-related disability in the United States.
-
Concussion
A concussion is the mildest form of TBI. It is the most common but least serious type of brain injury. Effects are usually temporary but can include headaches and problems with concentration, memory, balance and coordination.
-
Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI)
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is the stage between the expected cognitive decline of normal aging and the more serious decline of dementia. It’s characterized by problems with memory, language, thinking or judgment. Mild cognitive impairment may increase the risk of later developing dementia caused by Alzheimer’s disease or other neurological conditions.
-
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks cells in parts of the central nervous system – particularly the brain and spine – causing them to work less efficiently, or not at all.
MS can produce motor, sensory, and cognitive symptoms, as well as significant fatigue. Motor symptoms can include weakness or numbness/tingling in parts of the body. Sensory symptoms can include loss of vision or blurred vision. Cognitive symptoms include slowed thinking speed, difficulties paying attention, reduced recent memory, word finding, and trouble with problem solving. Visuospatial skills can be affected at times too. Emotional symptoms can also occur.
-
Parkinson’s disease
Cognitive impairments within Parkinson’s disease encompass a spectrum of difficulties associated with thinking, memory, and mental processing. These challenges can manifest alongside the motor symptoms of the condition and may involve issues with memory retention, attention, executive function, and the capacity to plan and coordinate tasks. While not universally experienced among those with Parkinson’s, cognitive problems can significantly impact daily functioning and should be closely supervised and addressed as an integral part of the overall treatment strategy.
-
Dementia
Dementia encompasses the progressive loss of cognitive abilities—thinking, remembering, and reasoning— to the extent that it disrupts daily life and activities. In some cases, individuals with dementia may experience emotional instability and undergo personality changes. Its severity spans a spectrum, from the initial stages with subtle effects on functioning to the advanced stages, necessitating complete assistance with basic daily activities.
Dementia can result from various diseases and injuries, either directly or indirectly affecting the brain, with Alzheimer’s disease and stroke being prominent contributors. Alzheimer’s disease, the most prevalent form of dementia, alone accounts for 60-70% of cases.
In the management of individuals with mild dementia, a holistic approach involves promoting physical, social, and mental engagement. Timely diagnosis is crucial as it can help mitigate the functional decline associated with cognitive impairment. Cognitive screening and training play pivotal roles in this process, aiding in early identification and targeted interventions.
-
Post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC)
The COVID-19 pandemic has affected millions of individuals across the country. While most individuals recover from the virus completely within a few weeks, many experience lasting effects of the virus for months.
For those experiencing persistent symptoms – whether following a prolonged hospital stay or recovery at home – rehabilitation may be beneficial in managing physical, cognitive and emotional deficits following recovery of the virus.
For individuals who have suffered a COVID-19-related stroke or neurologic injury, speech therapy can help improve communication and language skills. Speech therapy can treat cognitive symptoms such as impaired word retrieval, attention, and memory deficits associated with COVID-related neurologic syndromes.
-
Cerebral palsy (CP) with cognitive deficits
Cerebral palsy (CP) is associated with cognitive impairments, learning difficulties and reduced social participation. Individual assessment is necessary for individually tailored interventions. With the right set of cognitive therapies and interventions, a child can learn to work within his or her limits, which in turn extends his or her ability to function.
-
Cognitive symptoms post Chemotherapy
Chemo brain is a common term used by cancer survivors to describe thinking and memory problems that can occur during and after cancer treatment. Chemo brain can also be called chemo fog, cancer-related cognitive impairment or cognitive dysfunction. Signs and symptoms of chemo brain may include the following: Confusion, Difficulty concentrating, Difficulty finding the right word, Difficulty learning new skills, Difficulty multitasking, Short attention span, Short-term memory problems, Taking longer than usual to complete routine tasks, Trouble with verbal memory, such as remembering a conversation, Trouble with visual memory, such as recalling an image or list of words. Computer-aided cognitive training helps to strengthen cognitive abilities of people who have cognitive symptoms derived from chemotherapy.
Neurodevelopmental disorder

-
ADHD
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is one of the most common neurodevelopmental disorders of childhood. ADHD is often first identified in school-aged children when it leads to disruption in the classroom. Children with ADHD may have trouble paying attention, controlling impulsive behaviors, or be overly active.
ADHD can last into adulthood. Some adults have ADHD but have never been diagnosed. The symptoms can cause difficulty at work, at home, or with relationships. Symptoms may look different at older ages, for example, hyperactivity may appear as extreme restlessness. Symptoms can become more severe when the demands of adulthood increase.
Psychiatric disorders
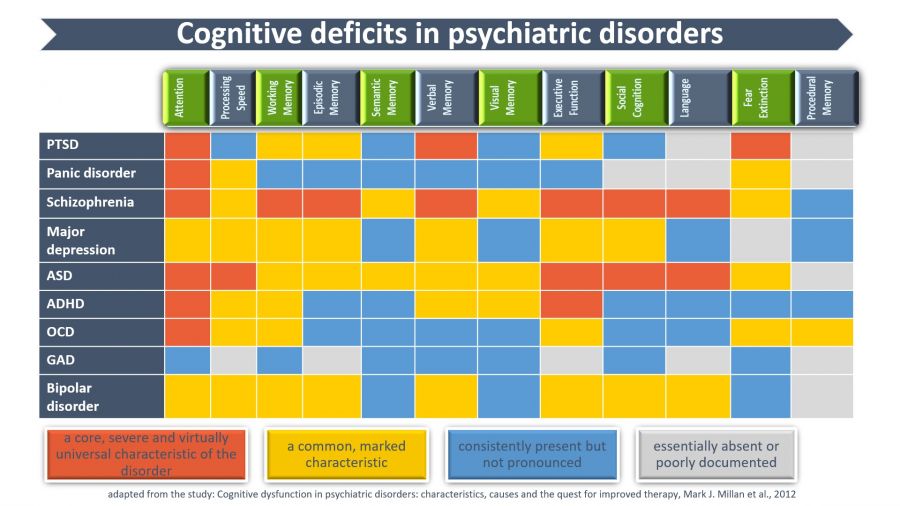
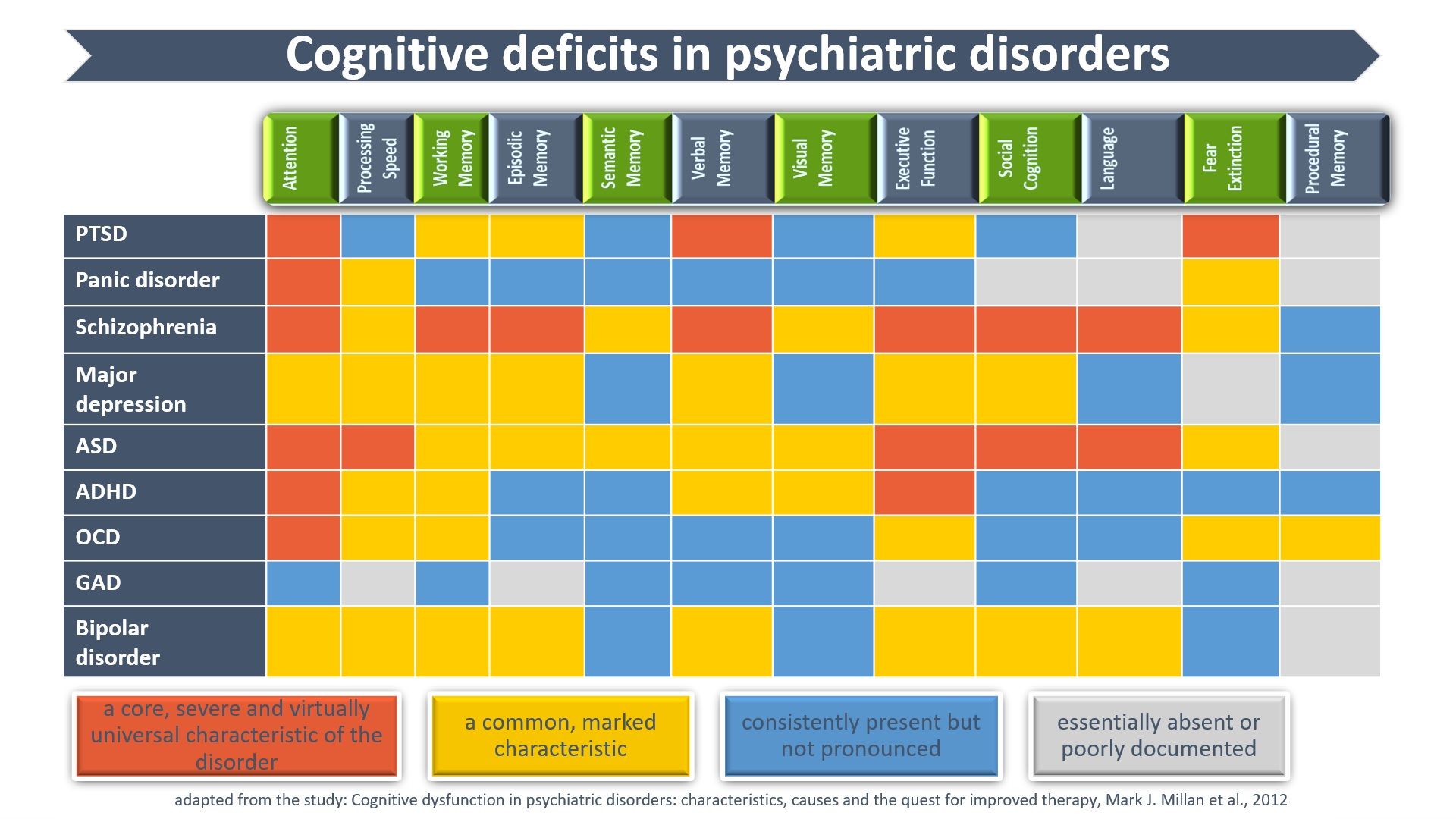
Deficits in cognitive function – ranging from decreased attention and working memory to disrupted social cognition and language – are common in psychiatric disorders.
Computer-aided cognitive remediation therapy was found to improve and correct cognitive performance and real-life functioning.
Psychiatric disorders are associated with complex and disease specific patterns of cognitive impairment. Certain cognitive impairments can be improved, rectified or compensated. A brief overview of the main characteristics of cognitive impairment in psychiatric disorders are displayed in this table.

HEADAPP
FREE TRIAL
No Credit Card required / No Obligation
- Try the full program for up to 14 days
- Free trial for the software on Windows and Mac PCs/Laptops
- Software loads in your default browser, no install needed
- Click “Professional Version” and “Register”
- Start by adding your first patient clicking “New”
GET STARTED TODAY